Knee pain is a widespread condition that affects individuals of all ages. It can be caused by an injury, excessive use of the knees, or by underlying medical conditions. Knee pain can make it difficult to do everyday tasks. In this blog, we will discuss the causes of knee pain, the symptoms associated with it, the diagnosis of knee pain, and its possible treatments.
Causes of knee pain

1. Injuries:
a) Sprains and strains: Sudden movement or trauma can cause ligaments (sprains) and muscles or tendons (strains) to stretch or tear, resulting in sprains and strains.
2. Joint Conditions:
a) Osteoarthritis: Over time, the knee joint’s cartilage wears down, causing pain, stiffness, and reduced mobility.b) Rheumatoid arthritis: It is an autoimmune disease that causes inflammation and pain in joints.
3. Mechanical Problems:
a) Meniscus Tears: The meniscus is a rubbery disc that support the knee and is prone to injury due to twisting movements.b) Patellofemoral Pain Syndrome: This results in pain around the kneecap due to overuse, injury, or misalignment.
4. Medical Conditions:
a) Gout: Uric acid crystals build up in the knee joints, leading to sudden and severe pain.
b) Infections: Knee pain and swelling can be caused due to bacterial or viral infections.
5. Overuse or Misuse:
a) Tendonitis: Inflammation of the tendons that surround the knee, that is commonly caused due to repetitive activity or overuse.
b) Bursitis: Inflammation of the bursae (fluid-filled sac) that cushion the knee joint results in bursitis.
6. Trauma:
a) Fractures: These result in broken bones in the knee that are usually caused due to severe impact or fall.
Understanding the different causes of knee pain is key to accurately diagnosing and treating knee pain.
Symptoms of knee pain
The location and intensity of knee pain can differ depending on the underlying cause. Symptoms commonly associated with knee pain include:
Pain: Knee pain is characterized by a range of symptoms, from a dull pain to a sharp, stabbing sensation. The degree and location of the pain can provide valuable information regarding the underlying cause of the pain, such as an injury, inflammation, or a long-term medical condition.
Swelling: Swelling around the knee joint is commonly referred to as effusion. This swelling is caused by the accumulation of fluid in the joint as a result of inflammation or injury, and can lead to stiffness in the knee, reducing its range of motion.
Stiffness: The knee is prone to stiffness, which makes movement difficult and often increases after periods of inactivity. Conditions such as arthritis can cause the knee to become less flexible, making bending or straightening the knee difficult.
Instability: Signs of knee instability or weakness are indicative of problems with the underlying structural components of the joint. Injuries to ligaments or joint conditions can weaken the stability of the knee, resulting in a sensation of displacement during movement.
Redness and Warmth: Inflammatory conditions may result in the knee becoming red and warm to the touch. These visual and tactile symptoms are caused by an increase in blood circulation to the affected area, which is often accompanied by pain and swelling.
Diagnosis of knee pain

Diagnosing knee pain based on its location is crucial for determining the underlying cause. Here's a concise overview:
1. Anterior knee pain: Pain that affects the front and center of the knee.
· Patients with patellofemoral pain syndrome may experience pain in the anterior part of the knee.
· This condition is commonly diagnosed using physical examinations, imaging tests (X-rays, MRI), assessing factors like gait and muscle strength.
2. Medial knee pain: Pain on the inner side of the knee.
· The medial knee pain is caused by medial meniscus tears and medial collateral ligament injuries.
· Diagnostic approaches include clinical evaluation, imaging studies, stress tests for ligament injuries.
3. Lateral knee pain: Pain on the outer side of the knee.
· This particular type of knee discomfort may be the result of lateral meniscus tears or lateral collateral ligament injuries.
· This is diagnosed using physical examination, imaging tests, assessing stability and range of motion.
4. Posterior knee pain: Pain behind the knee.
· Hamstring tendonitis or Baker's Cyst can cause pain in the back of the knee.
· This is diagnosed using clinical examinations, imaging tests (ultrasound, MRI), etc.
5. Generalized knee pain: Pain all around the knee.
· Causes of generalized knee pain include osteoarthritis and rheumatoid arthritis.
· Diagnosis of this condition is based on a comprehensive medical examination, which includes a physical exam, a blood test for inflammatory markers, and imaging tests.
6. Pain under the knee: Under the knee pain can be directly below the kneecap or further down in the leg to the shin or back to the calf.
· It may be caused due to conditions like tendonitis, bursitis, and bone spurs.
· This condition is diagnosed using physical examinations, imaging tests, as well as assessing aggravating activities.
7. Pain on top of the knee: Pain particularly above the knee/kneecap area or the lower thigh.
· It may be caused due to arthritis and soft tissue inflammation.
· Diagnostic approaches include clinical evaluation, assessing range of motion, and imaging tests, if required.
Knee pain can be diagnosed through a combination of patient’s medical history, a physical exam, and suitable imaging tests. Different diagnostic tools may be employed by healthcare professionals to determine the site and nature of the knee pain, enabling a personalized treatment plan to be developed based on the underlying cause.
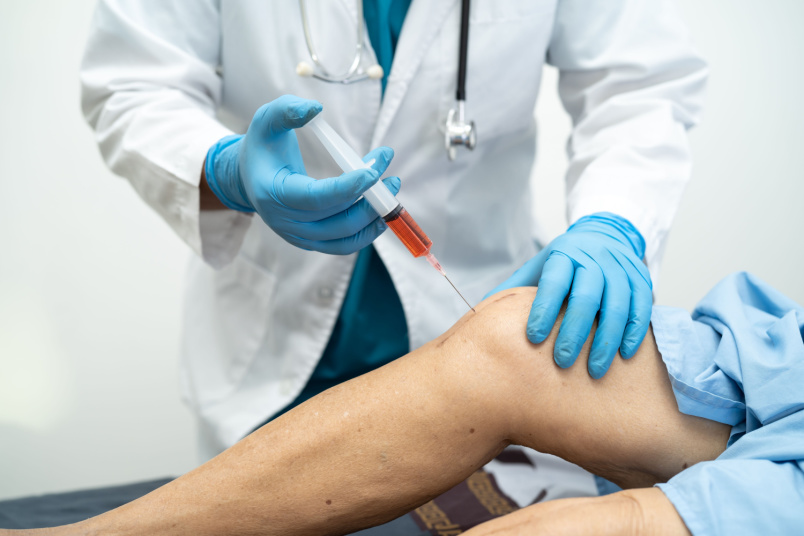
Healthcare providers will recommend treatment options based on the intensity of the pain and its underlying cause.
Rest and ice: Resting the knee facilitates the healing process, and the application of ice assists in the reduction of inflammation and pain. A cold pack or a cloth-wrapped ice pack can be applied for a period of 15 to 20 minutes every 2 to 3 hours.
Physical therapy: Customized exercises and stretches work to strengthen the ligaments around the knee joint, increasing flexibility and decreasing stress. Physical therapists work with patients to implement rehabilitation programs to improve joint function.
Pain medications: Pain relievers can alleviate knee pain and reduce inflammation.
Compression and elevation: Bandage compression helps to reduce swelling, while raising the knee above the heart helps to reduce fluid build-up.
Knee braces or supports: A wide range of knee braces offer stability, support, and compression to the knees. They can be especially useful for ligament injuries, providing relief during everyday activities or sports.
Corticosteroid injections: Corticosteroids administered directly to the knee joint can relieve pain associated with conditions such as arthritis and bursitis.
Weight management: Maintaining a healthy weight is essential for the long-term health of the knee joints, particularly those affected by conditions such as osteoarthritis, as it reduces the pressure on the knee joints. Proper diet and exercise are key components for maintaining a healthy weight.
Surgical interventions: Structural issues that contribute to knee pain can be addressed through surgical procedures such as arthroscopy, meniscus surgery, ligament reconstruction, or knee replacement.
Lifestyle modifications: Lifestyle modifications are necessary to reduce the impact on the knees. This can be achieved by engaging in low-impact activities such as swimming or cycling, as well as wearing the appropriate footwear. These changes can help to reduce the risk of knee pain and improve overall joint health.
In conclusion, addressing knee pain requires a multi-faceted approach, considering its diverse causes. From rest and physical therapy to medical interventions and lifestyle adjustments, tailored treatments aim to reduce pain and restore function to the knee. By seeking professional advice, it is possible to make a precise diagnosis and manage the condition effectively, thus contributing to the preservation of joint health in the long run.
KM NU Hospitals, Ambur offers state-of-the-art orthopaedic facilities, providing comprehensive services that include knee replacement surgery. Our experienced orthopaedic professionals and dedicated team are available to provide ongoing guidance throughout the entire treatment process, ensuring that patients receive the highest quality of care tailored to their individual needs.
Author: Dr. Tahir Ahmed
References:
1. Knee pain. MAYOCLINIC. https://www.mayoclinic.org/diseases-conditions/knee-pain/symptoms-causes/syc-20350849.
2. Knee Pain. Penn Medicine. https://www.pennmedicine.org/for-patients-and-visitors/patient-information/conditions-treated-a-to-z/knee-pain.
3. Knee Pain and Problems. JOHNS HOPKINS MEDICINE. https://www.hopkinsmedicine.org/health/conditions-and-diseases/knee-pain-and-problems.
4. Knee Pain. Cleveland Clinic. https://my.clevelandclinic.org/health/symptoms/21207-knee-pain.